Sensorimotor/Somatic OCD

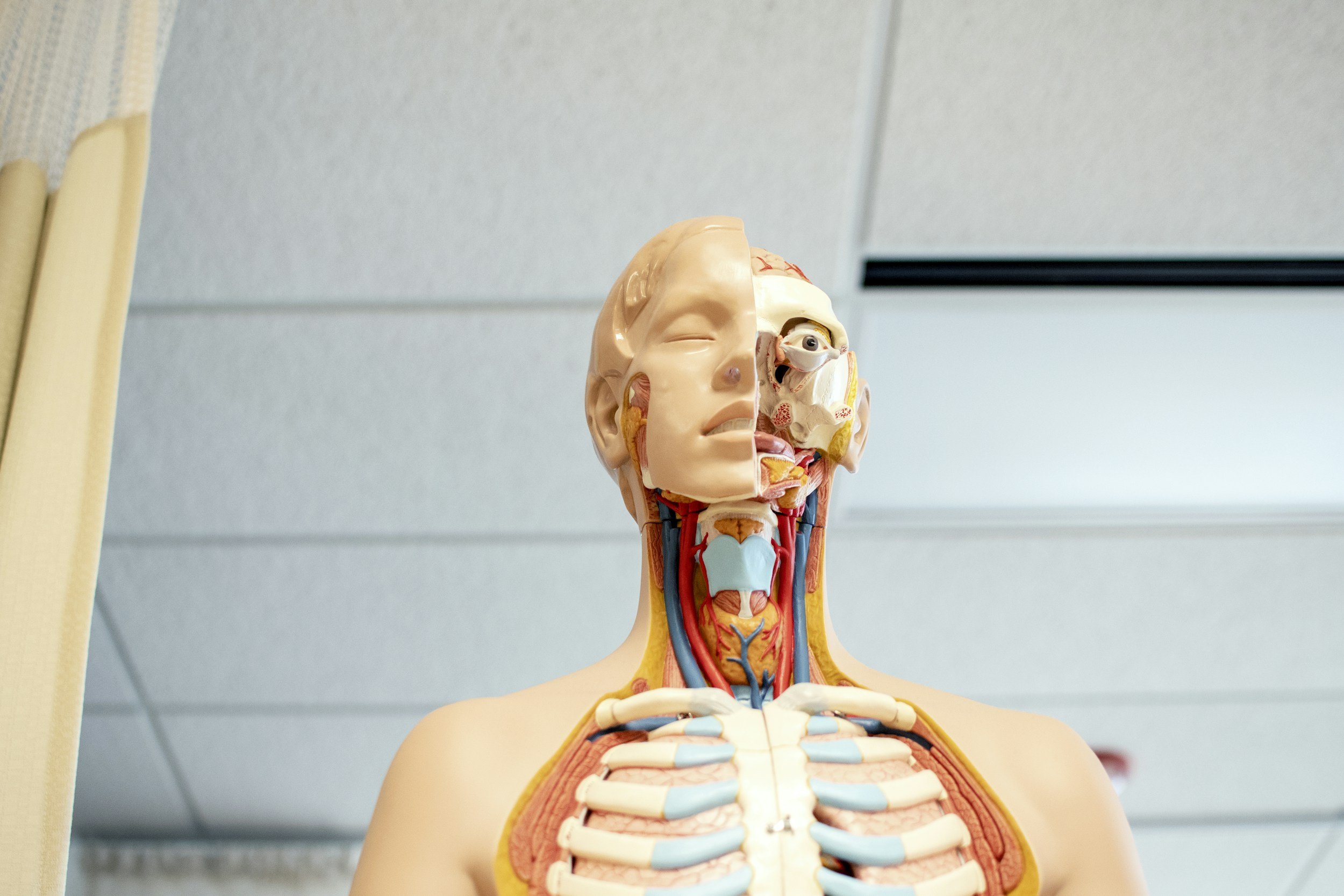
Sensorimotor or Somatic OCD is a subtype of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder characterized by hyperawareness and distressing preoccupation with bodily sensations or functions. Individuals with this form of OCD often experience intrusive thoughts about breathing, swallowing, blinking, or other bodily processes that are normally automatic.
These obsessions lead to compulsive behaviors such as constant monitoring of bodily sensations, seeking reassurance from doctors or others about physical health, avoiding activities that might exacerbate symptoms, or performing rituals to alleviate perceived bodily discomfort. Addressing Sensorimotor OCD involves recognizing the irrational nature of these fears and learning strategies to resist the compulsions and reduce the anxiety over time. This approach helps individuals regain control over their focus and live a more comfortable and fulfilling life.
-
Hyperawareness of bodily sensations: Constantly focusing on and monitoring bodily sensations, such as heartbeat, breathing, or digestion.
Fear of bodily dysfunction: Obsessive worries about bodily functions not working properly or fear of developing a serious illness or disease.
Fear of losing control over bodily functions: Anxiety about involuntary bodily actions or movements, such as blinking, swallowing, or muscle twitches.
Preoccupation with symmetry or alignment: Obsessions about body symmetry or alignment, feeling discomfort if body parts do not feel "right" or are not in a certain position.
Fear of bodily contamination: Concerns about bodily fluids, germs, or contamination leading to obsessive cleaning or avoidance behaviors.
Compulsive body checking: Repeatedly checking body parts or functions to ensure they are functioning normally or are in the correct position.
Excessive grooming: Engaging in excessive grooming or hygiene rituals to alleviate anxiety related to bodily sensations or appearance.
-
Excessive body checking: Repeatedly checking body parts or bodily sensations to ensure they are functioning correctly or to alleviate anxiety.
Seeking reassurance: Seeking reassurance from others or medical professionals about bodily symptoms or concerns.
Avoidance behaviors: Avoiding situations or activities that may trigger or exacerbate bodily sensations or obsessions.
Compulsive researching: Excessively researching medical conditions or symptoms online or in medical literature.
Compulsive grooming: Engaging in excessive grooming or hygiene rituals related to bodily sensations or appearance.
Monitoring behaviors: Constantly monitoring bodily functions, such as heart rate, breathing, or digestion, to check for abnormalities.
Compulsive movement: Performing repetitive movements or exercises to alleviate anxiety or discomfort related to bodily sensations.

